The Puzzle of Trying to Put an Object into a std::optional -- Raymond Chen
 The
The std::optional<T> is a powerful tool for handling optional values, but assigning non-trivial types like Doodad to it can lead to unexpected compilation errors. This post explores why such assignments fail and unpacks the nuances of std::optional and type construction in modern C++.
The Puzzle of Trying to Put an Object into a std::optional
by Raymond Chen
From the article:
The C++ standard library template type
std::has one of two states. It could be empty (not contain anything), or it could contain aoptional<T> T.Suppose you start with an empty
std::. How do you put aoptional<T> Tinto it?One of my colleagues tried to do it in what seemed to be the most natural way: Use the assignment operator.
struct Doodad { Doodad(); ~Doodad(); std::unique_ptr<DoodadStuff> m_stuff; }; struct Widget { std::optional<Doodad> m_doodad; Widget() { if (doodads_enabled()) { // I guess we need a Doodad too. Doodad d; m_doodad = d; } } };Unfortunately, the assignment failed to compile:
 In this article, we'll learn about
In this article, we'll learn about  While most time zones use simple hour offsets from UTC, some regions have chosen unusual time differences. In this blog post, we’ll explore how we can discover such zones using C++20’s chrono library.
While most time zones use simple hour offsets from UTC, some regions have chosen unusual time differences. In this blog post, we’ll explore how we can discover such zones using C++20’s chrono library.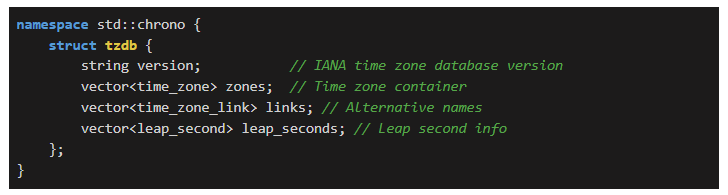
 In this blog post, we will explore handling dates using std::chrono, including time zones. We’ll utilize the latest features of the library to retrieve the current time across various time zones, taking into account daylight saving time changes as well. Additionally, we will incorporate new capabilities introduced in C++23, such as enhanced printing functions and more.
In this blog post, we will explore handling dates using std::chrono, including time zones. We’ll utilize the latest features of the library to retrieve the current time across various time zones, taking into account daylight saving time changes as well. Additionally, we will incorporate new capabilities introduced in C++23, such as enhanced printing functions and more. Recent versions of the C++ language (C++20 and C++23) may allow you to change drastically how you program in C++. I want to provide some fun examples.
Recent versions of the C++ language (C++20 and C++23) may allow you to change drastically how you program in C++. I want to provide some fun examples. Programming at compile time has been possible in C++ for a long time. Wu Yongwei considers its past, present and future.
Programming at compile time has been possible in C++ for a long time. Wu Yongwei considers its past, present and future. Probably the two most useful features added to C++20 are
Probably the two most useful features added to C++20 are