Making C++ Safer -- Greg Law
Should you start new projects in C++, these days? Is language safety an issue for you? What can be done, today?
Making C++ Safer
by Greg Law
From the article:
I believe that over time C++ will become a lot safer, maybe even some kind of ‘safe’. Competition is good: Clang was the best thing to happen to GCC, and Rust might turn out to be the best thing to happen to C++. That journey has already begun, with proposals for the evolution of the language including Contracts and Profiles, and simply changing some of the defaults in C++26. While the language custodians work to make the language itself safer, what can you do today?

 When using std::atomic<std::shared_ptr<T>>, the C++ standard defines a "change" as a modification to either the stored pointer or the control block pointer. However, since atomic wait mechanisms typically track only a single memory address, the Microsoft implementation handles this limitation by using a timeout-based polling strategy to detect changes in the control block.
When using std::atomic<std::shared_ptr<T>>, the C++ standard defines a "change" as a modification to either the stored pointer or the control block pointer. However, since atomic wait mechanisms typically track only a single memory address, the Microsoft implementation handles this limitation by using a timeout-based polling strategy to detect changes in the control block.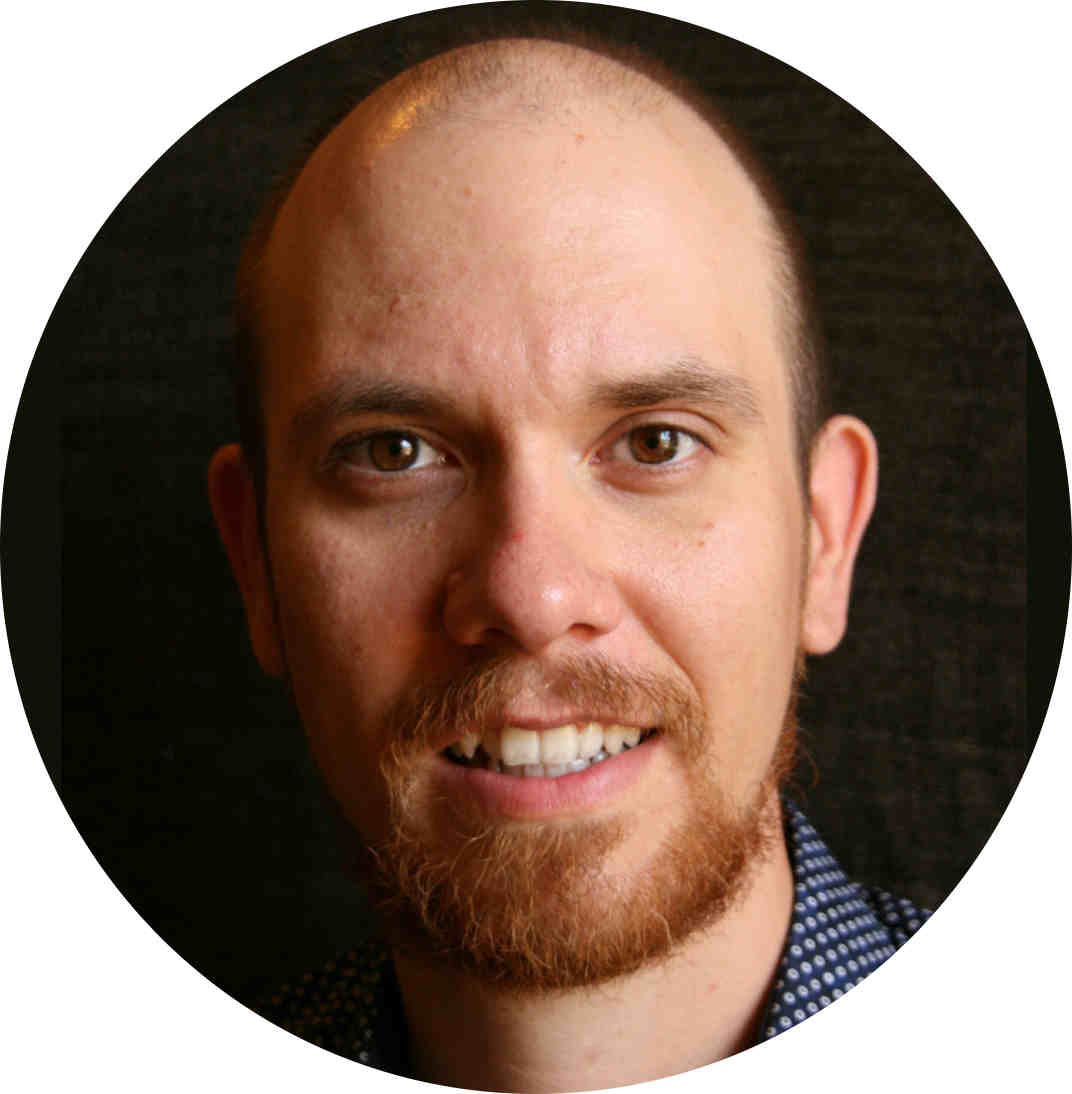 In this post, we are going to discuss a core language feature proposed by Corentin Jabot and Micheal Park in P2169R4. With the new standard we get a cool unnamed placeholder.
In this post, we are going to discuss a core language feature proposed by Corentin Jabot and Micheal Park in P2169R4. With the new standard we get a cool unnamed placeholder. Since its introduction, the
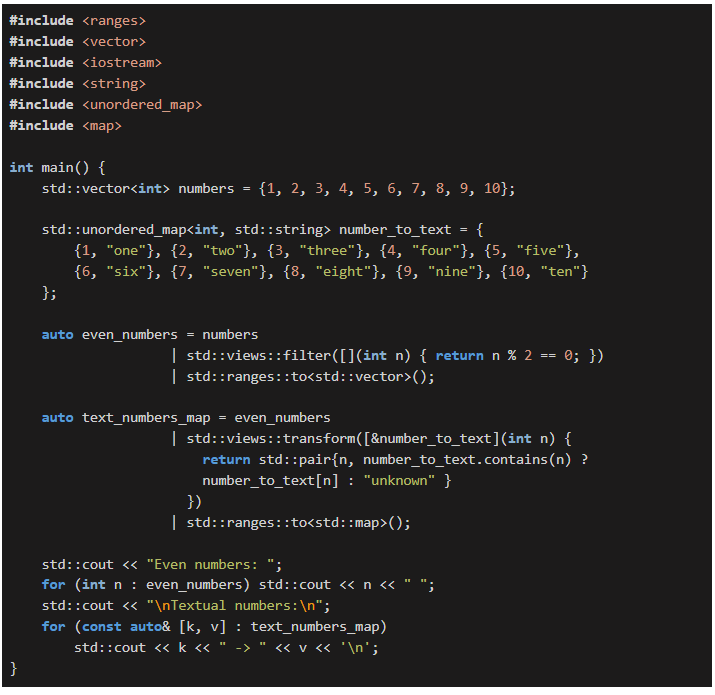
Since its introduction, the  Sometimes, we all need a way to iterate over a container in the opposite direction. There are several ways to reverse-iterate a container, and in this article, we’ll explore them.
Sometimes, we all need a way to iterate over a container in the opposite direction. There are several ways to reverse-iterate a container, and in this article, we’ll explore them. In this article, you’ll see eight larger examples that illustrate the changes in C++23.
In this article, you’ll see eight larger examples that illustrate the changes in C++23.