Concurrency Patterns -- Rainer Grimm
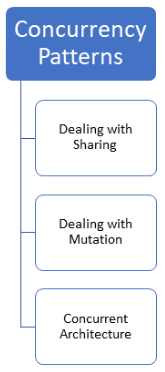 There are many well-established patterns used in the concurrency domain. They deal with synchronization challenges such as sharing and mutation but also with concurrent architectures. Today, I will introduce and dive deeper into them in additional posts.
There are many well-established patterns used in the concurrency domain. They deal with synchronization challenges such as sharing and mutation but also with concurrent architectures. Today, I will introduce and dive deeper into them in additional posts.
Concurrency Patterns
by Rainer Grimm
From the article:
The main concern when you deal with concurrency is shared, mutable state or, as Tony Van Eerd put it in his CppCon 2014 talk “Lock-free by Example”: “Forget what you learned in Kindergarten (ie stop Sharing)”. A crucial term for concurrency is a data race. Let me first define this term.
- Data race: A data race is when at least two threads access a shared variable simultaneously. At least one thread tries to modify the variable. If your program has a data race, it has undefined behavior. This means all outcomes are possible, so reasoning about the program makes no sense anymore.
A necessary condition for a data race is a mutable, shared...

 Nico Josuttis gave a talk recently that included an example and I wanted to explain what’s going on in this example, what the issue is, and what (if anything) is broken.
Nico Josuttis gave a talk recently that included an example and I wanted to explain what’s going on in this example, what the issue is, and what (if anything) is broken. Registration is now open for CppCon 2023! The conference starts on October 1 and will be held
Registration is now open for CppCon 2023! The conference starts on October 1 and will be held  Registration is now open for CppCon 2023! The conference starts on October 1 and will be held
Registration is now open for CppCon 2023! The conference starts on October 1 and will be held  C language was defined to cover a large range of computer architectures, including many which would be considered museum relics today. It therefore takes a very conservative view of what is permitted, so that it remains possible to write C programs for those ancient systems. (Which weren’t quite so ancient at the time.)
C language was defined to cover a large range of computer architectures, including many which would be considered museum relics today. It therefore takes a very conservative view of what is permitted, so that it remains possible to write C programs for those ancient systems. (Which weren’t quite so ancient at the time.) Registration is now open for CppCon 2023! The conference starts on October 1 and will be held
Registration is now open for CppCon 2023! The conference starts on October 1 and will be held